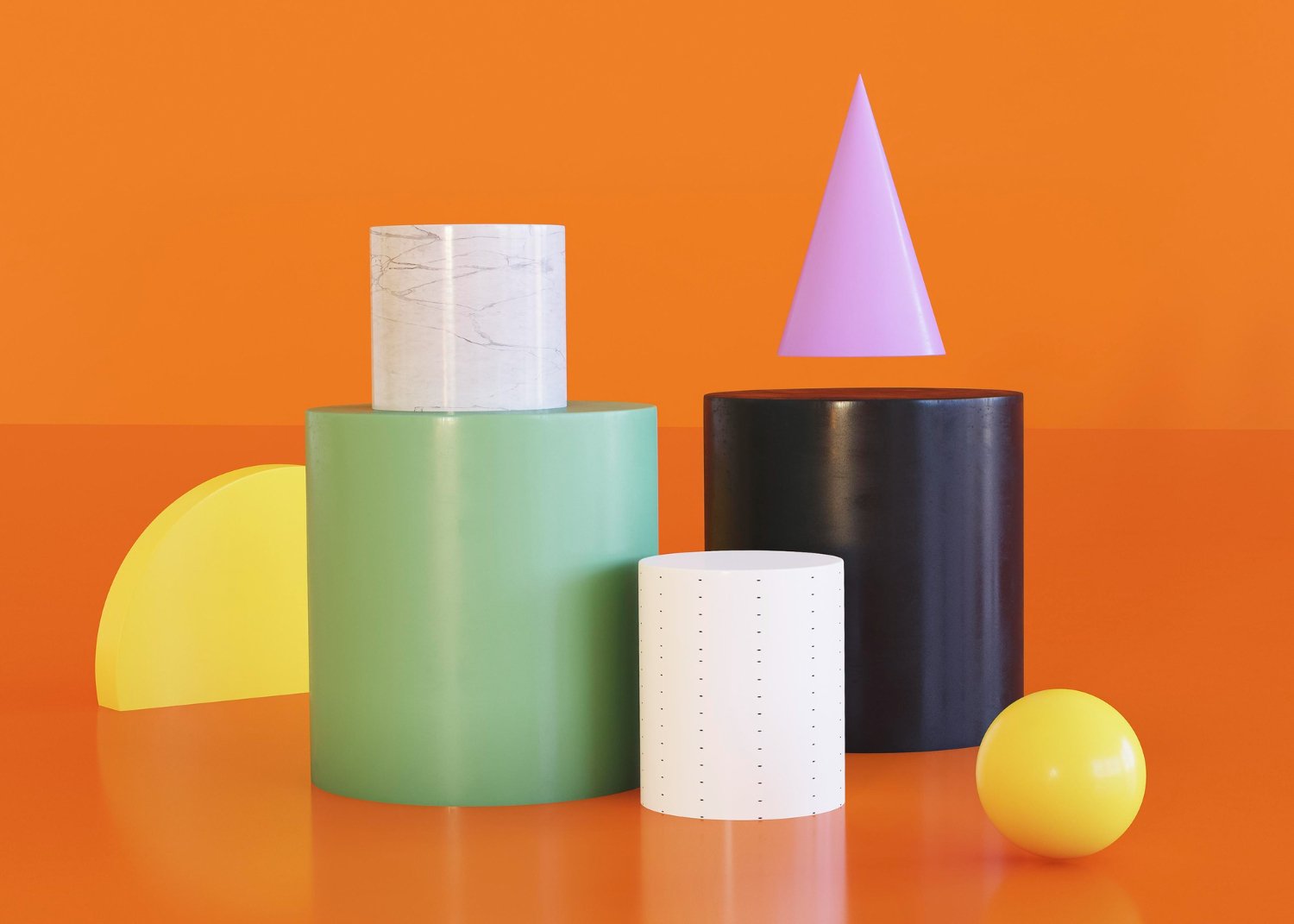
3D Product Modelling
Craft stunning 3D models of everyday objects and cutting-edge tech with our intensive course. Master lighting, texturing, and rendering to create compelling visuals for marketing, e-commerce, and design portfolios.
Build professional 3D product showcases in our 4-week course
Designed for aspiring 3D artists, this comprehensive four-week course on Seed LMS guides you step-by-step through Autodesk Maya, Arnold Renderer, and modern AI workflows. You will develop the essential skills of high-fidelity hard-surface modelling, realistic surfacing, studio lighting, and technical animation while building a professional product rendering pipeline. Beyond the core four weeks, you’ll receive a full month of free, one-on-one mentorship to polish your final renders, troubleshoot your meshes in real-time, and confidently build your 3D portfolio. Choose from our curated pool of 10 exciting product briefs, refine your skills, and graduate with two portfolio-ready product showcases.
Course Outline
Week 1: Precision Modelling & Topology
Topic A: Reference & Scale
- Importance of real-world measurements.
- Setting up Image Planes and orthographic views.
- Project Management: Incremental saves and scene organisation.
Topic B: Hard Surface Modelling Workflow
- Sub-division surfaces vs. Low-poly modelling.
- Support Loops and Holding Edges: Controlling sharpness in smoothed meshes.
- Bevels and Fillets: Replicating manufactured edges.
Topic C: Advanced Topology
- The “All-Quad” Rule: Avoiding N-Gons on curved surfaces.
- Booleans and Clean-up: Using Booleans effectively and fixing the resulting topology.
- Flow Retopology: Redirecting edge loops for complex cut-outs (e.g., button holes).
Week 2: Lookdev & Surfacing
Topic A: UV Mapping for Products
- Unfolding complex shapes without distortion.
- UDIM vs. Layout: Organising UV shells for high-resolution labels.
- The “Relax” and “Straighten” tools for clean texture application.
Topic B: Shaders & Materials (Arnold)
- Standard Surface: Mastering IOR (Index of Refraction) for glass and plastic.
- Anisotropy: Creating the “brushed metal” look for electronics.
- Clear Coat and Sheen: Simulating car paint and fabric.
Topic C: Labels & Decals
- Using AI (Gemini) for branding: Generating fictional product names and logo concepts.
- Layering Textures: Placing logos over materials using Alpha maps.
Week 3: Studio Lighting & Presentation
Topic A: Product Photography Principles
- 3-Point Studio Lighting: Mastering Key, Fill, and Rim lighting roles.
- Softboxes and Reflectors: Using Arnold Area Lights with custom textures for appealing highlights.
Topic B: The Virtual Camera (Pushes, Pulls, and Orbits)
- Focal Length: Using long lenses (85mm–100mm) to avoid product distortion.
- Camera Animation:
- The Push-In: Slow, purposeful movement towards a detail.
- The Pull-Back: Starting on a detail and revealing the full product scale.
- The Orbit: A smooth, cinematic move around the subject to show form and volume.
Topic C: Technical Presentation (Turntables & Exploded Views)
- The 360° Turntable Render:
- Setting up a seamless rotation.
- Graph Editor Mastery: Converting tangents to Linear to ensure a perfectly looping animation without “easing.”
- The Animated Exploded View:
- Hierarchy & Parenting: Organising parts for independent movement.
- The Reveal: Animating individual components “exploding” outwards to show internal engineering.
- Staggered Animation: Offsetting keyframes so the explosion feels organic.
Week 4: AI Workflow & Rendering
Topic A: Innovative AI Workflow (Using Gemini)
- The Conceptual Partner: Using Gemini to generate fictional product briefs or “backstories.”
- The Technical Advisor: Asking Gemini to troubleshoot Maya errors or Arnold render artefacts.
- AI for Environment: Using Gemini to describe a perfect 3D environment to inform your lighting.
Topic B: Arnold Render Settings
- Sampling and Noise: Getting rid of “fireflies” and grain.
- AOV (Arbitrary Output Variables): Exporting passes for post-processing.
Topic C: Final Output
- Batch Rendering the turntable and exploded view.
- Encoding: Using Media Encoder to create a high-quality MP4/MOV file.
Mentorship
- Portfolio Review: One-on-one sessions to polish your renders for ArtStation.
- Career Advice: How to find work in Product Design and Advertising agencies.
What’s Inside?

1-on-1 Mentorship
One full month of dedicated expert guidance tailored to your specific goals.

Seed LMS Access
Lifetime access to the Student Portal, hosting all your modules and resources.
Weekly Interactive Quizzes
Test your skills and track progress with gamified assignments and feedback.

Official Certification
Validate your expertise with a digital certificate recognized by industry leaders.
What You Will Learn
- Apply precision sub-division modelling and maintain clean edge flow for hard surfaces
- Unwrap complex shapes and map high-resolution labels without UV distortion
- Create high-end Arnold materials like brushed metal, glass, and clear-coat plastics
- Set up professional 3-point studio lighting to mimic real-world product photography
- Animate cinematic camera moves, seamless 360° turntables, and complex exploded views
- Utilise AI tools to generate product branding, troubleshoot errors, and speed up workflows
- Render high-quality, portfolio-ready product showcases and animated sequences




